Value Added Tax (VAT) in UAE
Germany and France are the two countries who introduce the VAT system the first time. They are the pioneer of implementation of Value Added Tax (VAT) as a general consumption tax during the World War. The VAT was implemented with modern variations for the first time in the 1950s.
Value Added Tax (VAT) in the UAE, is a type of general consumption tax which is imposed by government incrementally based on the value added at each stage of production or sales of goods and services. It is an indirect tax also known as consumer tax. It is collected at each stage of the supply chain where the end users have to ultimately pay the tax.
In UAE, VAT is imposed from 1st January 2018 with the standard rate of 5%. GCC (Gulf Cooperation Council) have agreed to apply VAT in the region at a standard rate 5% in the GCC VAT agreement. In GCC, UAE and Saudi Arabia will be first two countries to impose VAT from 1st January, while other member countries of GCC will follow the same in coming years. VAT is implemented in almost all type of daily basic consumable goods and services.
The implementation of VAT will provide the source of income to the government of UAE that will be utilized to provide a high quality of public services. It will also help UAE government to reduce dependency on oil and other hydrocarbons as a source of revenue. In the UAE with levied VAT, It is estimated that the government revenue will be increased by almost AED 12 billion in the first year 2018 and AED 20 billion in the second year 2019.
The vice president and prime minister of UAE and the ruler of Dubai, Sheikh Mohammad bin Rashid Al Maktoum has been announced that the 70% of the revenue of VAT will be going to local government and this would be used to improve the local services, community development and to improve the living standard of residents. The remaining 30% revenue will go to the federal budget.
UAE impose VAT on minimum rate while other countries levied VAT on high rates. The implementation of VAT will be resulting in the form of high prices of goods and services. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) has estimated that the UAE inflation will be reached to 3.6 percent in this year 2018 that is higher than the 2.8 percent of the previous year 2017. High prices have an impact on the cost of living of residents. According to experts, residents with lower income less than AED 5000 will not have much more impact of the VAT. While middle-class residents with earning AED 20,000 have more impact on their cost of living because their expenses will be increased. However, higher income residents have also no impact on VAT implementation because of the minimum rate of the VAT.
However, the ministry has announced that if any retailer or supplier will raise the price of taxable goods and services more than the levied rate of VAT, he will be liable to pay a heavy fine of AED 100,000.
VAT implementation:
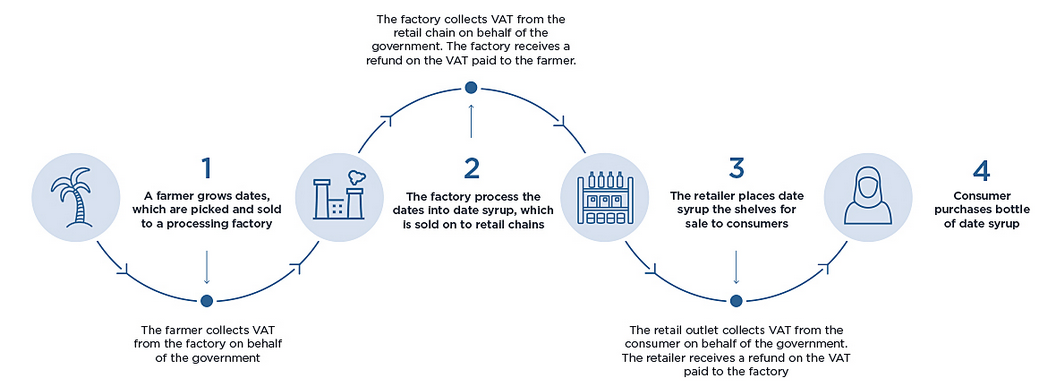
VAT is implemented on each step of the supply chain of goods and services. While end users bear the cost of VAT and the registered businesses collect and liable for the tax and act in the way as tax collector on the behalf of Federal Tax Authority. The below diagram shows that how VAT works step by step:
 VAT Registration:
VAT Registration:
In UAE, All businesses are liable to make registration for VAT which exceeds mandatory or voluntary registration threshold.
Mandatory Threshold:
A business must be registered if the value of its taxable supply exceeds from the mandatory threshold (AED 375,000) over the previous 12 months or on the forecasted supply of next 30 days.
Voluntary Threshold:
Any business may apply to register voluntarily for VAT if it does not meet the mandatory threshold. It would be registered if the value of its taxable supplies or expenditures exceed from the voluntary threshold (AED 187,500) in the last 12 months or predict that it will be exceeded in the next 30 days.
The following sales of goods and services are to be considered for arriving the mandatory or voluntary threshold:
Standard rate supplies: it includes the list of all types of goods and services that is taxable on the rate of 5% such as cars, smartphones, jewelry, eating outs, watches and entertainment etc.
Exempted supply: an exempt supply is a supply of those goods and services on which VAT tax is not levied and for which the related input tax is not deductible.
Exempted supplies sectors are included:
- Local passenger transport
- Bare land (that has no building on it)
- Certain financial Services
- Supply of residential buildings
Zero Rated supply: A zero-rated supply is a taxable supply of goods and services on which tax is charged at 0% and for which the related input tax is deductible.
It includes sectors of:
- Crude oil and natural gas
- Medicine and medical equipment
- Healthcare services
- Investment in gold, silver, and platinum
- Exports
- Residential buildings(first sale or lease within 3 years)
- International transport of passenger and goods
- Certain Education services
A business can be registered directly for VAT with HMRC (Her Majesty’s Revenue and Customs). However, people face problems and issues because of unawareness of the registration system so the majority of people find an agent to make this process easier. Any business can also assess the Federal Tax Authority’s online portal https://eservices.tax.gov.ae/en-us/ for online registration for VAT.
Calculation of VAT:
 The manufacturer spends (AED 1× 1.05) = AED 1.05 for the raw materials and seller of raw materials pays the government AED 0.05.
The manufacturer spends (AED 1× 1.05) = AED 1.05 for the raw materials and seller of raw materials pays the government AED 0.05.- The manufacturer charges the retailer (AED 1.10× 1.05) =AED 1.16 and pays the government (AED 0.055– 0.005) = AED 0.005
- The retailer charge the consumer (AED 1.21× 1.05) = AED 1.27 and pays the government (AED 0.06 –0.055) = AED 0.005
VAT is ultimately collected from the consumers through the businesses.
